News
At the 23rd Annual Meeting of the Japanese Society of Anti-Aging Medicine, Dr. Reimi Yoshigata gave a presentation on "New Perspectives on Women's Health Care from the Perspective of Female Aging and Microbiome Changes"
Dr. Reimi Yoshigata, special advisor to the Midtown Clinic (chief of women's medical research) and obstetrician-gynecologist, said at the 2023rd General Meeting of the Japanese Society of Anti-Aging Medicine held on Friday, June 6, 9,"New Perspectives on Women's Health Care from the Perspective of Female Aging and Microbiome Changes"He gave a presentation entitled:
Four doctors, including Dr. Yoshigata Reimi, gave presentations on their respective areas of expertise at the "Female Menopause Symposium (Chairman's Symposium 4)."
Presentation by Dr. Reimi Yoshigata
The human microbiome network
The human body comes into contact with the outside world from the sterile environment of the womb at birth, and immediately after birth, the entire body (i.e. skin, oral cavity, nasal cavity, intestines, vagina, etc.) is exposed to microorganisms. After that, the bacterial flora suited to the environment settles and forms the resident bacterial flora in each part of the body.
"Microbiome" is a concept that includes the genetic information of microorganisms, and refers to the environment in which a population is placed (microflora). A gradual movement in research into "microbiota" (microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses) began in the 1960s, and the concept of "microbiome" was proposed in 2001. Over the past 20 years, research into the microbiome has progressed rapidly due to advances in genetic analysis.
The microbiome shares space within the human body and is an unwitting determinant of our health and disease. The human microbiome, which exists in the body, has functions such as "regulating the immune system," "nutrient breakdown metabolism," and "hungry satiety signaling," and is most abundant in the digestive tract (intestine).
The microbiome has both positive and negative effects on the body.In the vagina, Lactobacillus species are involved in reducing the risk of pathogens, sexually transmitted diseases, premature birth, and gynecological cancer.In addition, it is closely related to female hormone-like effects."Equol-producing bacteria" have been found in large numbers among opportunistic and beneficial intestinal bacteria.
Women's health and the intestinal microbiome: Equol production and intestinal flora
The effects of equol include "relief of menopausal symptoms," "inhibition of bone loss after menopause," and "reduced risk of breast cancer and prostate cancer."
[Case Study]
- <Comparative study on the effect of equol production on reducing the risk of lifestyle-related diseases>
└The superiority of equol production, especially in women in their 50s and 60swas shown.
└In people who can produce equol, compared to those who cannot,
- -"Body fat" and "visceral fat" area
- - Bone resorption marker
- -Parameters related to arteriosclerosis
- - Uric acid level
- - Inflammation markers
The results showed significantly lower values in the
- For more information,Click here for the result press release (PDF: 356KB) .
- <Survey results on the relationship between equol production, intestinal flora, and dietary and lifestyle habits>
└Equol-producing bacteria were found in all subjects.97% of the population had equol, but only 22% of them were equol producers.Met.
It was suggested that many people who have equol-producing bacteria are not working.
└It was shown that the strongest factor behind the activity of equol-probiotics was the diversity of intestinal bacteria.
- <Comparison of dietary habits between equol producers and non-producers>
It was found that dietary habits such as the consumption of root vegetables and mushrooms, which are rich in dietary fiber, and light-colored and yellow-green vegetables, as well as a regular intake of protein such as fish and soy products, as well as exercise habits, are involved in the ability to produce equol.
Smoking, eating out, infrequent or frequent bowel movements, and dietary habits high in alcohol, coffee, and ramen have been shown to be related to non-production of equol.
Women's health and the vaginal microbiome - Changes in the vaginal microbiome throughout the life cycle
It is said that an ideal vaginal environment is one in which there is an abundance of lactic acid bacteria, mainly "Lactobacillus". After menopause, the vaginal microbiome changes significantly due to a decrease in estrogen. In the field of molecular research, the vaginal microbiome is classified into five communities, CST I to CST V, and CST IV is the type with the least amount of Lactobacillus and is a diverse group that contains many pathogenic bacteria and has a negative effect on the female body. It is known that in women's life stages, the most Lactobacillus is present in the vagina during sexual maturity when estrogen levels are at their highest, and after menopause, the number of Lactobacillus decreases and changes to diversity.
The amount of lactobacillus in the vagina also changes depending on the menstrual cycle. During menstruation, estrogen levels decrease, so there is less lactobacillus and the pH level increases, creating a vaginal environment that is favorable for the proliferation of bacteria.
It is also known that the more lactobacillus is prevalent in the vagina, the lower the risk of infection with sexually transmitted diseases such as HPV, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and trichomoniasis, while the greater the diversity of vaginal bacteria, the higher the risk of infection with these diseases. In addition to cervical cancer, it is also known that the state of the vaginal bacterial flora affects the carcinogenesis mechanisms of uterine cancer and ovarian cancer.
Exploring the crosstalk between vaginal and intestinal microbiota
Fetuses grow in a germ-free environment in the womb, and newborns acquire Lactobacillus from the mother's intestines. Previous research has shown that many bacterial flora (microbiomes) in the vagina and intestines of adults share a common genotype. It is also known that Lactobacillus, a beneficial bacteria present in the vagina, originates from the intestines. In this way, the bacterial flora in the vagina and intestines crosstalk with each other, exerting various metabolic functions and immune responses in the body.
[Case Study]
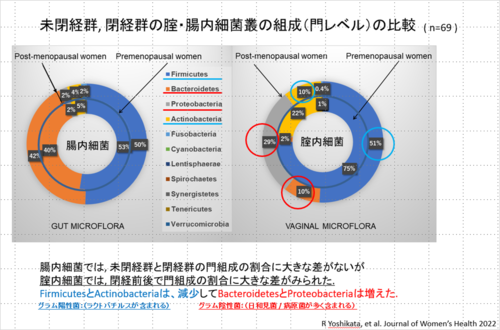
- <Study on aging-related changes in vaginal and intestinal bacterial flora and influencing factors and crosstalk>
- There was no significant difference in the proportion of intestinal flora between the menopausal and premenopausal groups.
In the vaginal flora,Pathogens and other germs increased in the menopausal group.
└The relationship between vaginal and intestinal microbiome crosstalk has been demonstrated.The influence of crosstalk is particularly strong in the menopausal group(After menopause, vaginal lactobacilli decrease, but this study demonstrated that the presence of vaginal lactobacilli after menopause is of intestinal origin.)
- It was shown that equol production ability may contribute to an increase in the Lactobacillus rate in the premenopausal group.
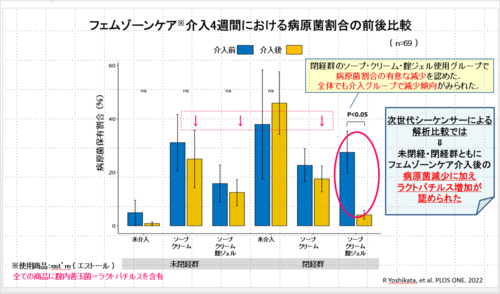
- <GSM by Femzone Care, a material containing Lactobacillus lactic acid bacteria※ 1Study on improvement effects and changes in vaginal microbiome
└A decrease in the proportion of pathogenic bacteria was observed in all groups, both menopausal and non-menopausal.Use of soaps, creams, and even vaginal gels, especially in the menopausal group※ 2Then,Significant reduction in pathogens in the Femzone care groupwas recognized.
└Overactive bladder symptom scores also improved significantlyWas done.
- For more information,Click here for the press release (PDF: 1.35MB) .
*1 Abbreviation for Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause, which in Japanese is translated as "menopause-related urogenital syndrome."
*2 [Products used]
Estol® Delicate Soft Wash | Estol® Delicate Soft Gel Cream
Estol® Inner Gel containing Lactobacillus lactic acid bacteria
A review of the benefits of probiotics on the vaginal microbiome concluded:OralThe purpose of using probiotics is said to be so that lactobacillus travels through the gastrointestinal system, from the rectum to the vagina (= the effect of vaginal-intestinal crosstalk).
moreover"TransvaginalThe administration of probiotics has been shown to have a direct effect on improving vaginal bacteria. Therefore, caution is required in the general use of antibacterial agents that disrupt the vaginal microbiome for vaginitis, cystitis, etc.
New perspectives on women's health care based on the microbiome
The concept of microbiome crosstalk between organs throughout the body, including the vagina and intestines, is attracting attention as a new treatment strategy.
This study found that crosstalk between the vagina and the intestine is particularly intense after menopause.Good postbioticsIt is important to maintain a lifestyle that produces "Lactobacillus" in the intestines. It is also important to continually use Femcare products that contain Lactobacillus as a "vaginal probiotic" to maintain the good bacteria "Lactobacillus" in the vagina.
As a comprehensive women's health care measure, it is very important to nurture the microbiome, which is considered to be good bacteria in the vagina and intestines.
*The content of this page is current as of July 2023, 7.