News
Vol.20 (2021/04/22) Antibody-positive patients at our clinic / Mutant viruses / Latest trends in Japan and the world / Degree of vaccine resistance to mutant viruses / Taiwan's containment policy, etc.
As you know from daily reports, the fourth wave is on the way.
The number of new infections in Osaka and Hyogo prefectures has exceeded the number of cases during the third wave when a state of emergency was declared, and even in the metropolitan area, including Tokyo, we cannot allow ourselves to let our guard down.
It is believed that this is due to the influence of a mutated virus, but we will take a closer look at whether vaccination is effective against the mutated strain.
It is expected to take some time before the vaccine is available to the entire population.
We would like to take advantage of previous overseas cases and the knowledge gained from them to work toward preventing infection.
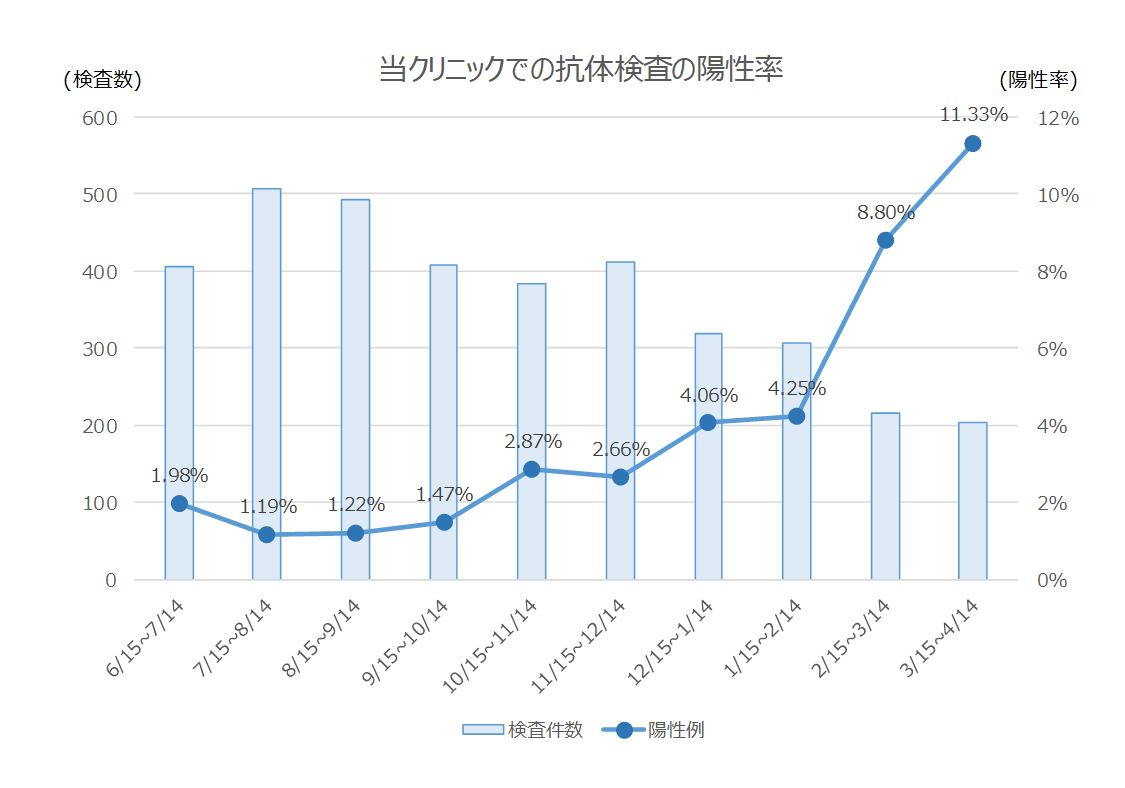
[1] The antibody positivity rate at our clinic is rising sharply.
当クリニックでは発熱や咳などの症状がない(過去2週間以内にもなかった)方を対象に実施しておりますが、2021年2月15日から2021年3月14日までのコロナ抗体陽性率は8.8%(19/216)でした。
そして2021年3月15日から2021年4月14日までのコロナ抗体陽性率は11.3%(23/203)と、とうとう2桁台になりました。
Asymptomatic infections are spreading steadily.
Figure 1: Positive rate of COVID-XNUMX antibody tests at our clinic
[2] Information on mutant viruses
As reported daily in the news, the proportion of mutated viruses is rapidly increasing even in Tokyo.
Figure 2: Incidence rate of mutant strains in Tokyo (survey by Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Public Health)
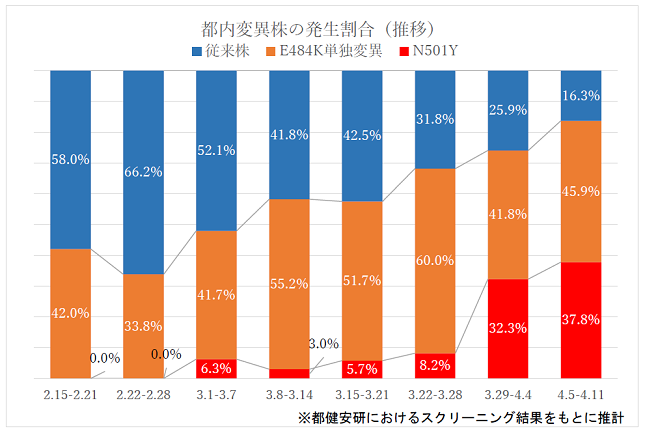
Source: Tokyo Metropolitan Government Bureau of Social Welfare and Public Health "Rate of occurrence of mutant strains in Tokyo"
https://www.fukushihoken.metro.tokyo.lg.jp/iryo/kansen/screening.html
Osaka Prefecture is ahead of Tokyo in terms of the incidence of mutant virus cases.
Results were reported for three days from April 4th to 9th.
According to the report, of the 2561 new infections during this period, or approximately 2%, of samples from 535 people were examined, and 443 of them, or 82.8%, were found to be mutated viruses.
大阪府の検査では▽3月25日までの1週間は43.2%、▽4月1日までの1週間は67.8%、▽4月8日までの1週間は78.5%となっていて、変異ウイルスの割合が徐々に高まっています。
Source: NHK News "Osaka: Mutation virus in over 4% of test subjects in the three days leading up to April 11"
https://www3.nhk.or.jp/news/html/20210415/k10012975481000.html
The Advisory Board, an expert group that advises the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, has estimated that the proportion of people infected with the mutated virus will increase over time.
Figure 3: Projected increase in the proportion of infected people with mutant strains (as of April 2021, 4)
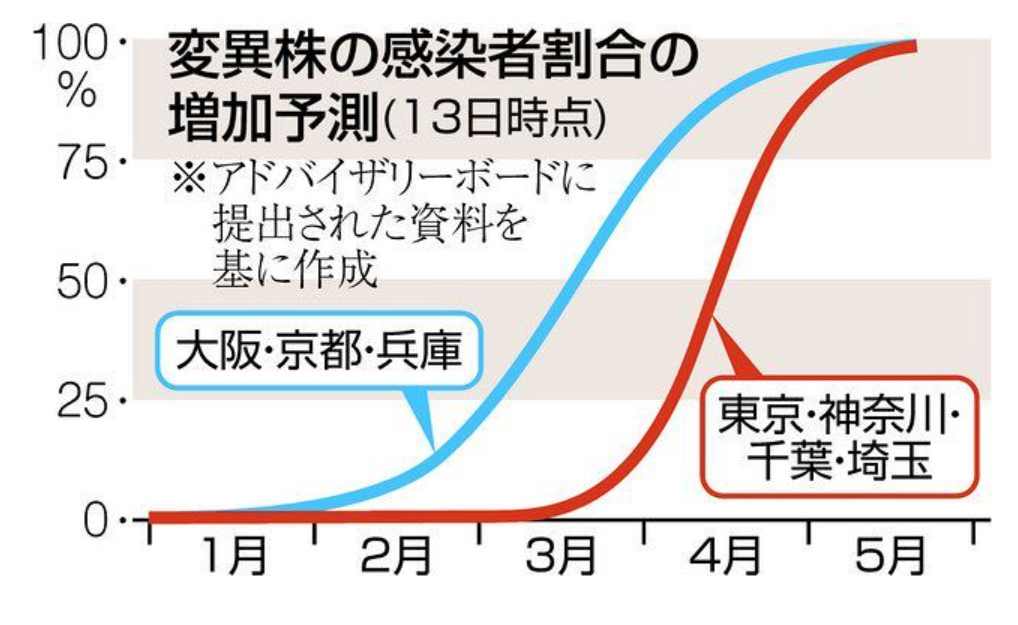
Source: Tokyo Shimbun "Are mutant strains more likely to become severe? Are the infection rates different? Expert opinions <New Coronavirus>"
https://www.tokyo-np.co.jp/article/98385
[3] Latest situation in Japan
Currently, the number of new infections nationwide is about half of the peak of the third wave, but the number of serious cases is on track to exceed 3% of that of the third wave.
Figure 4: Number of new positive cases, cumulative deaths, and number of serious cases (as of April 2021, 4)
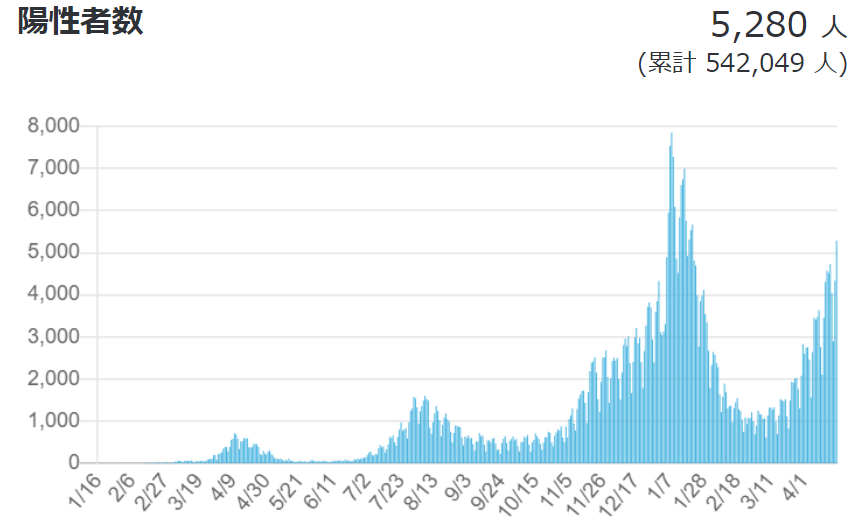
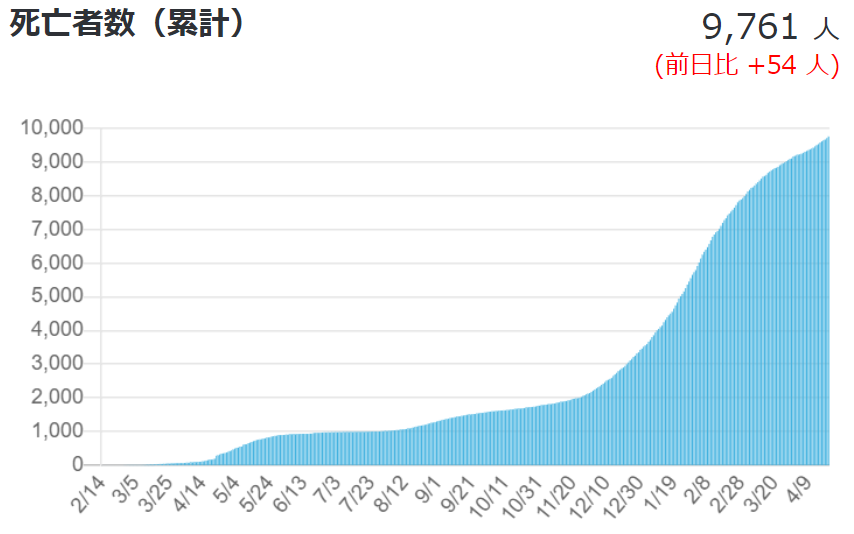
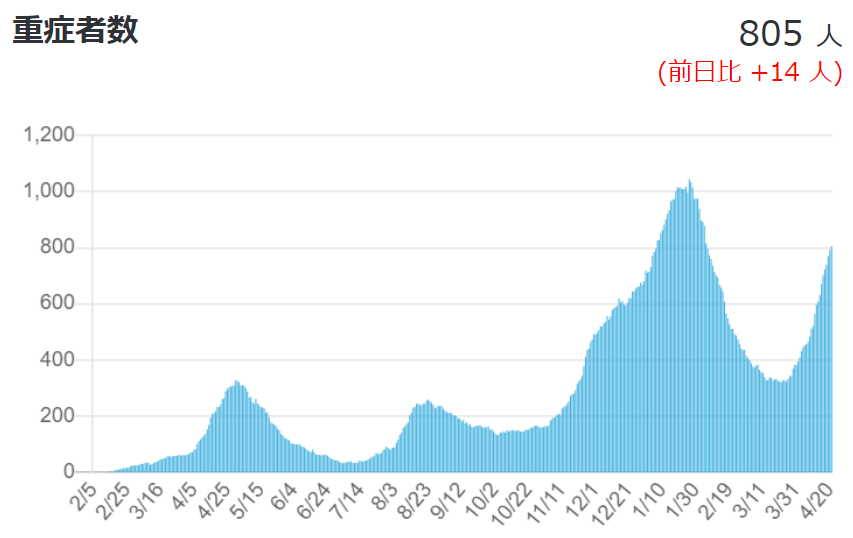
Source: Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, "Domestic outbreak situation" (as of April 2021, 4)
https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/covid-19/kokunainohasseijoukyou.html#h2_1
[4] Latest global situation
In the UK, where vaccination has progressed, new cases and deaths have dropped dramatically and are now at the same level as or lower than Japan.
Figure 5: Number of new deaths (as of April 2021, 4)
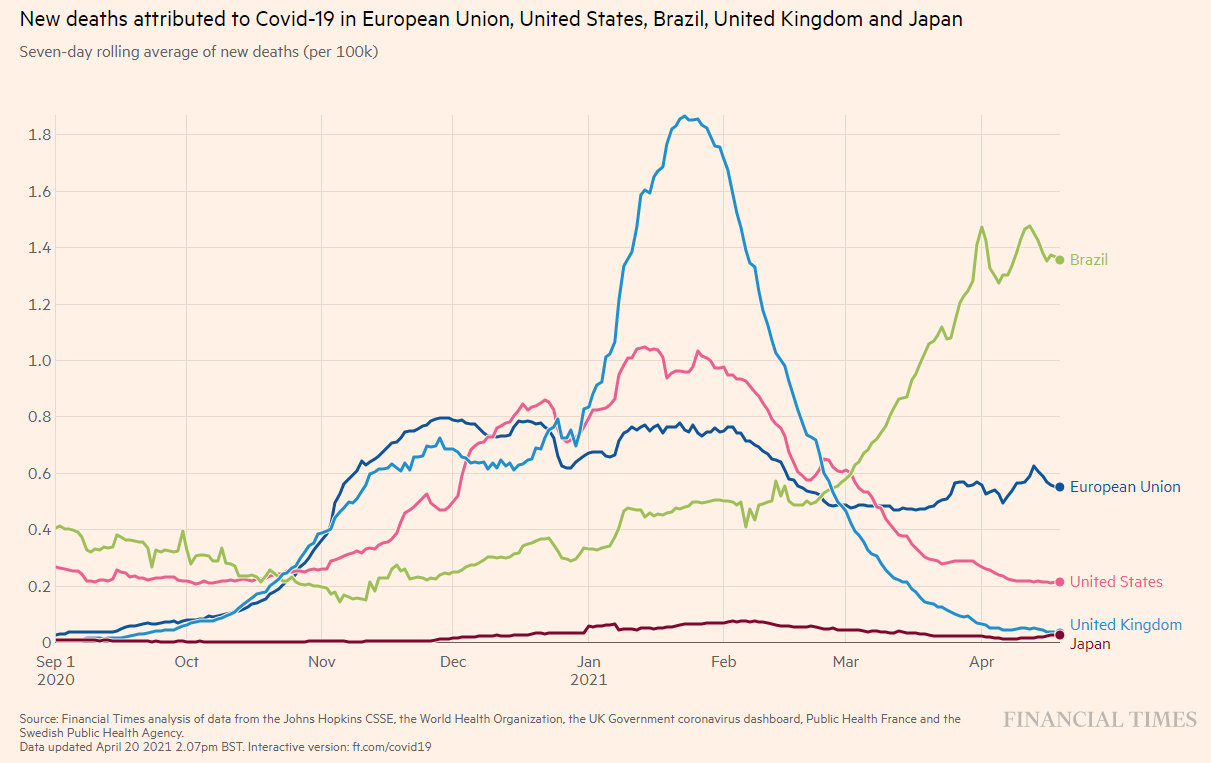
Source: FINACIAL TIMES: Coronavirus tracked: see how your country compares
https://ig.ft.com/coronavirus-chart/?areas=eur&areas=usa&areas=bra&areas=gbr&areas=jpn&areasRegional=usny&areasRegional=usnj&areasRegional=usaz&areasRegional=usca&areasRegional=usnd&areasRegional=ussd&cumulative=0&logScale=0&per100K=1&startDate=2020-09-01&values=deaths
Figure 6: Number of new infections (as of April 2021, 4)
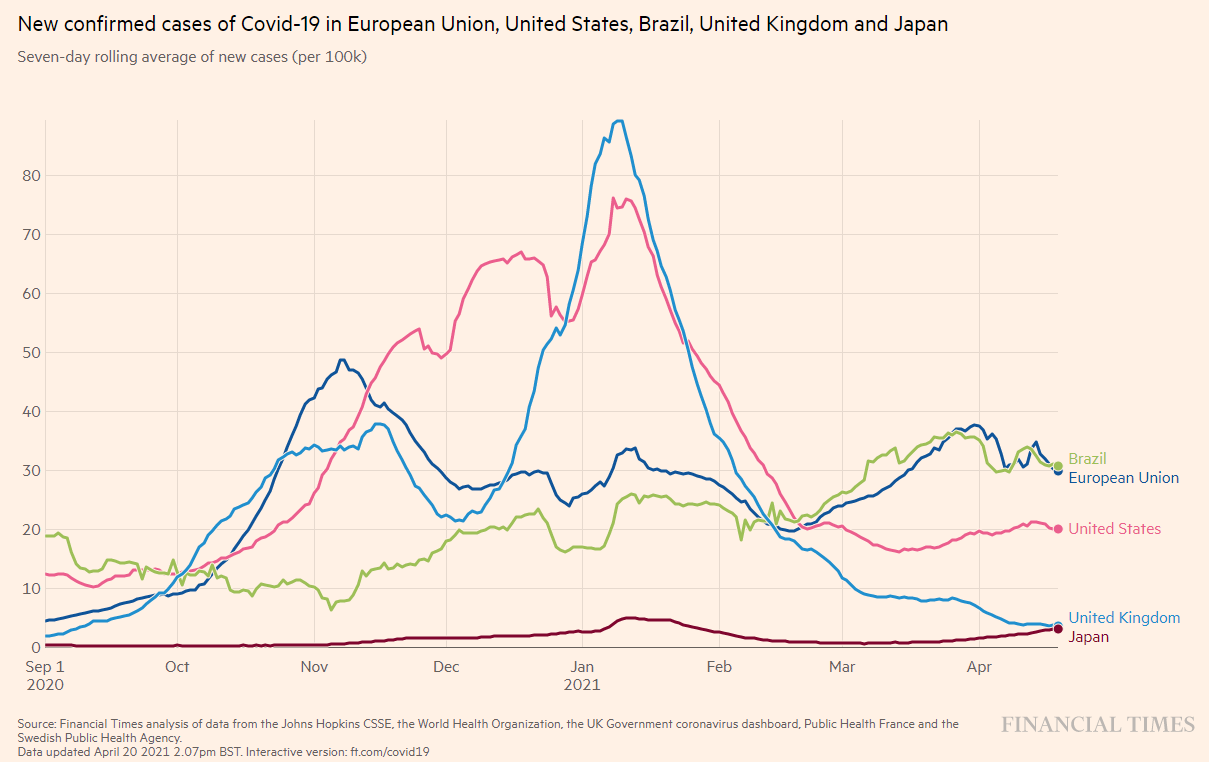
Source: FINACIAL TIMES: Coronavirus tracked: see how your country compares
https://ig.ft.com/coronavirus-chart/?areas=eur&areas=usa&areas=bra&areas=gbr&areas=jpn&areasRegional=usny&areasRegional=usnj&areasRegional=usaz&areasRegional=usca&areasRegional=usnd&areasRegional=ussd&cumulative=0&logScale=0&per100K=1&startDate=2020-09-01&values=cases
■ Comparison in Asia
India is experiencing a rapid recovery, and Japan and Thailand are also seeing increases.
Asia is not entirely safe.
Figure 7: Number of new infections (as of April 2021, 4)
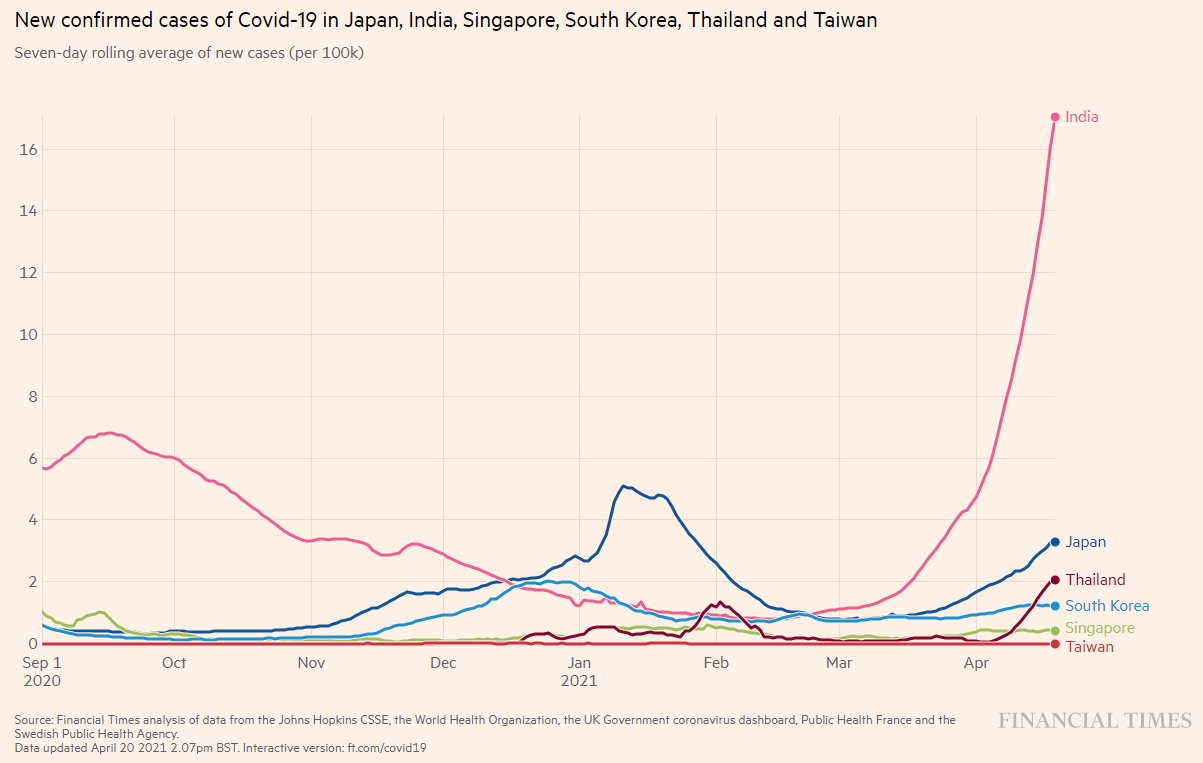
Source: FINACIAL TIMES: Coronavirus tracked: see how your country compares
https://ig.ft.com/coronavirus-chart/?areas=jpn&areas=ind&areas=sgp&areas=kor&areas=tha&areas=twn&areasRegional=usny&areasRegional=usnj&areasRegional=usaz&areasRegional=usca&areasRegional=usnd&areasRegional=ussd&cumulative=0&logScale=0&per100K=1&startDate=2020-09-01&values=cases
[5] Global vaccine situation
For example, how many vaccines have been administered per 100 people, and the percentage of people who have completed both doses.
We can see that Japan is quite far below.
Figure 8: Global vaccination status (as of April 2021, 4)
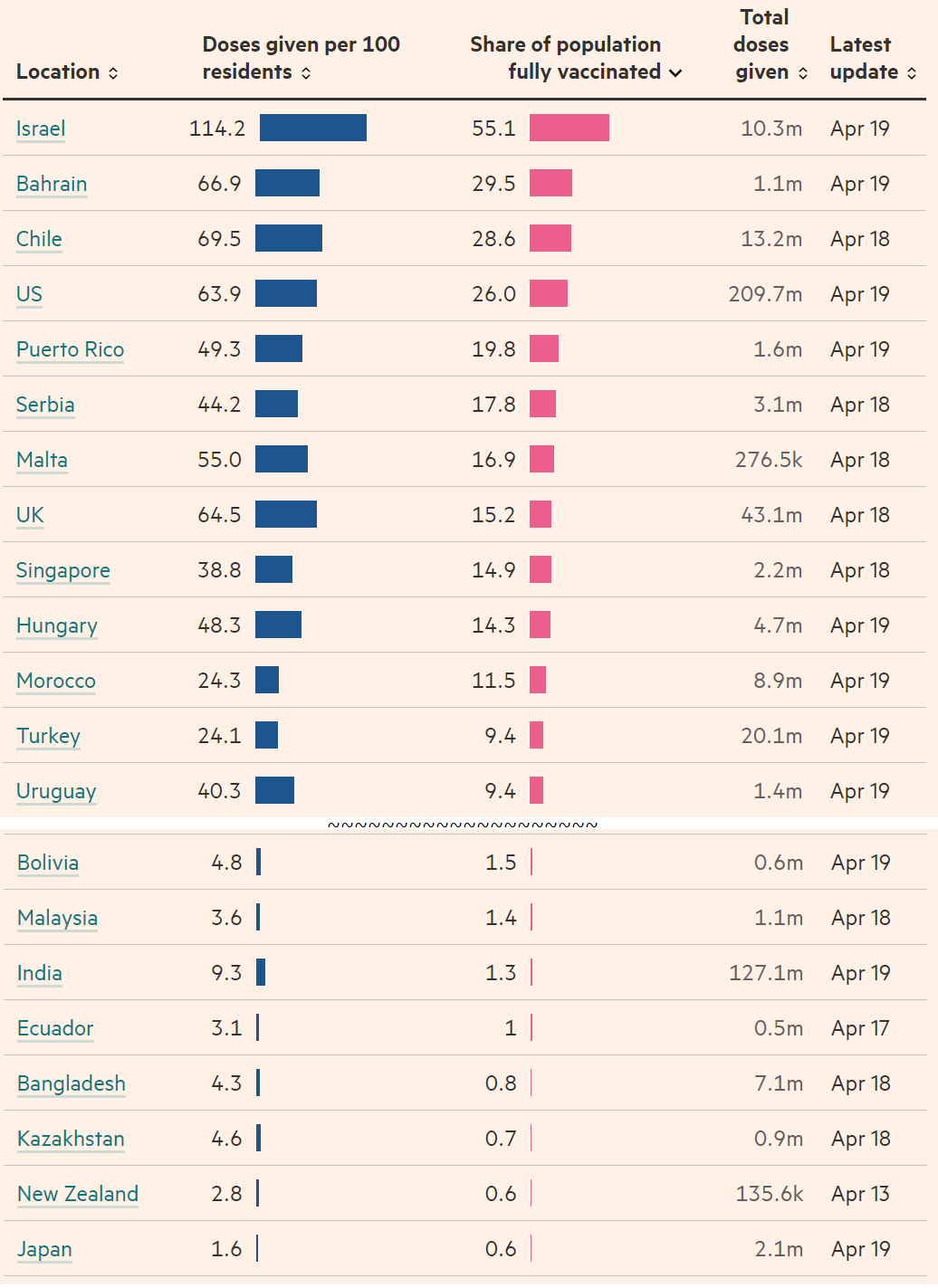
Source: FINACIAL TIMES “Covid-19 vaccine tracker: the global race to vaccinate”
https://ig.ft.com/coronavirus-vaccine-tracker/?areas=gbr&areas=isr&areas=usa&areas=eue&cumulative=1&populationAdjusted=1
[6] Vaccine response to mutated viruses (Moderna)
It has been reported that people who received the Moderna vaccine were able to produce neutralizing antibodies against the following typical mutant viruses (B.1, B.1.1.7, N501Y).
This is more than 10 times the amount of antibodies produced by a person with natural infection.
Figure 9: Neutralizing antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 variants (vaccinated individuals)
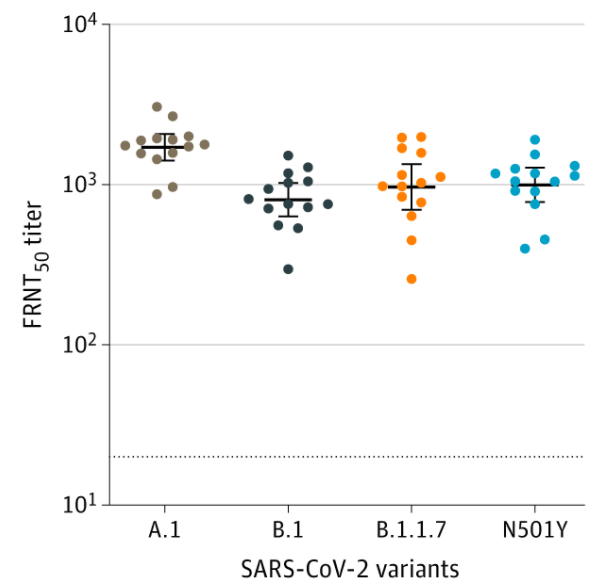
Source: JAMA Online
“Neutralizing Antibodies Against SARS-CoV-2 Variants After Infection and Vaccination” Published online March 19, 2021. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.4388
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2777898
[7] Vaccine response to mutated viruses (Pfizer)
Similarly, it has been reported that the Pfizer vaccine was able to produce antibodies against various mutant viruses (B.1.1.7, B.1, P.351). Again, after vaccination (the far right of each figure), the antibody titer increased by more than 1 times compared to natural infection (the far left of each figure).
Figure 10: SARS-CoV-2 infection and neutralization responses against the virus and variants following one dose of the Pfizer vaccine
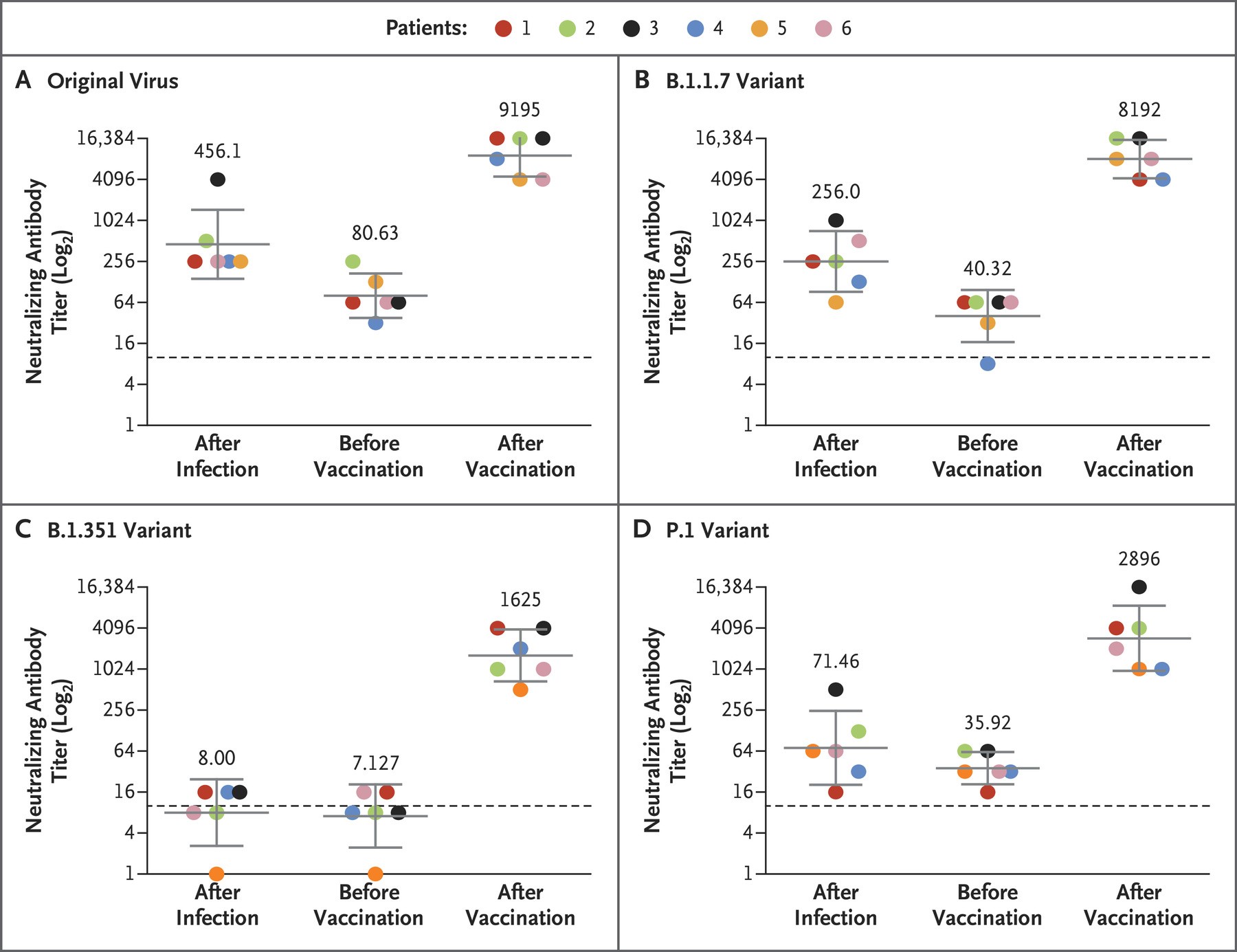
Source: NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL of MEDICINE
“Neutralizing Response against Variants after SARS-CoV-2 Infection and One Dose of BNT162b2”
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMc2104036
[8] Frequency of anaphylaxis after vaccination in Japanese people
Regarding the Pfizer vaccine, which has begun to be administered to medical workers, there have been many reports of side effects after vaccination.
However, when examined according to international standards, the number of cases of anaphylaxis is limited to 100 per 81 million vaccinations. Let's take a closer look.
The Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare held a specialist committee meeting on March 3th to discuss side effects that occurred after vaccination with the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-26) vaccine Tojinameran (brand name Comirnaty). The ministry announced that 2 people had been vaccinated between February 2th and March 17st, and 3 cases of suspected anaphylaxis were reported. When these cases were evaluated according to international standards (Brighton classification), 21 cases were found to be anaphylaxis, about half of whom had a history of allergies to foods, medicines, etc., and about 57% had asthma. The majority of cases have improved.
■ 100 cases per 81 million vaccinations, higher than Europe and the US
国内のトジナメラン接種者におけるアナフィラキシーの発現率はおよそ1万2,000回接種に1件、100万回当たり81件で、米国の4.7件、英国の19.4件を上回るが、接種総数など複数の理由から単純な比較は難しいとしている。発生頻度は女性で高いとされているが、今回の報告でもアナフィラキシーが生じた47例中44例(94%)が女性であった。Looking at the medical history and underlying diseases of the 47 cases, 23 cases (49%) had a history of allergies to medicines (contrast media, etc.), food, animals, etc. Apart from that, there was one case each of a history of anaphylaxis to food, animals, and pesticides, and a history of an allergy to pesticides. In terms of underlying diseases, the most common was bronchial asthma in nine cases, followed by hay fever in five cases, chronic urticaria, atopic dermatitis in two cases each, and high blood pressure in one case. Three cases had a history of asthma, including childhood asthma.
■People with a history of severe hypersensitivity to medicines containing polysorbates should also be careful.
The cause of Tojinamelan-induced anaphylaxis is believed to be polyethylene glycol (PEG), which is used to maintain the water solubility of the lipid bilayer membrane that forms the lipid nanomolecules in which the vaccine's active ingredient, mRNA, is encapsulated.Tojinameran is the first vaccine containing PEG in Japan, but there are concerns about cross-reactivity with PEG, and there are several vaccines in Japan that contain polysorbate, which has a structure similar to PEG. In addition to vaccines, polysorbate is also used as an emulsifier in various foods.
The guidelines "Management, diagnosis, and treatment of severe hypersensitivity (anaphylaxis, etc.) associated with COVID-2021 vaccines" formulated by the Japanese Society of Allergology and published on March 3, 1, state that people with a history of severe hypersensitivity to drugs containing PEG or polysorbates that are cross-reactive with PEG should avoid receiving Tosinamelan unless they are properly evaluated by a specialist and have a system in place to adequately respond to the onset of severe hypersensitivity such as anaphylaxis. "Severe hypersensitivity" is defined as the presentation of multiple symptoms that suggest anaphylaxis, such as anaphylaxis or systemic skin and mucous membrane symptoms, wheezing, dyspnea, tachycardia, and decreased blood pressure.
If delayed local reactions (erythema, induration, pruritus, etc.) occur after the first vaccination, a second vaccination is possible. On the other hand, if severe hypersensitivity occurs after the first vaccination, "the vaccination should be avoided."
Source: Medical Tribune "Anaphylaxis occurs 1 in 2,000 times"
Delivered November 2021, 04 02:18
https://medical-tribune.co.jp/news/2021/0402535895/
[9] Thrombosis after COVID-19 vaccine
A research report has revealed that a side effect of AstraZeneca vaccination is thrombosis accompanied by a decrease in platelets. Let's take a closer look.
Research background: Naturally occurring vaccine-associated variants of HIT
Two reports (from Germany and Norway) on vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT), which results in thrombosis (mainly cerebral venous thrombosis and visceral venous thrombosis) and thrombocytopenia after vaccination with AstraZeneca's ChAdOx1 nCov-19 vaccine, have been published in N Engl J Med (online April 2, 2021 and online April 4, 9).VITT has a pathology similar to that of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT), and appears to be classified as a vaccine-associated variant of naturally occurring HIT.
Key point: Immune thrombocytopenia occurs after vaccination
In Germany and Austria, 1 patients developed thrombosis or thrombocytopenia after receiving the ChAdOx19 nCov-11 vaccine (N Engl J Med online version April 2021, 4). Nine of the 9 patients were women, and the median age was 11 years (range 9-36 years). All patients, except for one patient who presented with a fatal intracranial hemorrhage, experienced one or more thrombotic events 22-49 days after vaccination.
Of the 1 patients who experienced one or more thrombotic events, 11 had cerebral venous thrombosis, 9 had visceral venous thrombosis, 3 had pulmonary embolism, and 3 had other thrombotic events. Six patients died. Five developed disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC).Meanwhile, in Norway, five health care workers aged 2 to 1 years were admitted to Oslo University Hospital with venous thrombosis and thrombocytopenia 19 to 7 days after the first dose of ChAdOx10 nCoV-32 adenoviral vector vaccine against SARS-CoV-54 (N Engl J Med online version April 5, 2021). Four cases had cerebral venous thrombosis and one case had visceral venous thrombosis. Four cases were treated with intravenous immunoglobulin, and three cases (a 4-year-old woman, a 9-year-old woman, and a 4-year-old woman) died.
■ Discussion: Attention must also be paid to thrombosis caused by the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine
On April 4, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) concluded that thrombosis accompanied by thrombocytopenia should be listed as a "very rare adverse reaction" for the AstraZeneca vaccine. Thrombosis has been reported to occur in women under the age of 7 within two weeks of vaccination.On April 4, the UK government decided not to recommend vaccination for people under the age of 7. By the end of March, 30 million doses of the AstraZeneca vaccine had been administered in the UK, and 3 cases of thrombocytopenia-associated cerebral venous thrombosis, 2,020 cases of other thrombosis, and 79 deaths had occurred.
In addition, on April 4, the EMA reported four cases of thrombosis and thrombocytopenia after vaccination with the Johnson & Johnson SARS-CoV-9 vaccine (three in the United States, one in a clinical trial and one death).
Features of VITT
① Onset approximately 1-19 weeks after receiving AstraZeneca's ChAdOx1 nCov-2 vaccine
② Occurs after the first vaccination (occurrences after the second vaccination are limited)
3) Cerebral venous thrombosis and visceral venous thrombosis are the main causes, and pulmonary embolism and arterial thrombosis may also occur.
④ It is more common in young women (mostly under 60 years old)
な ど
Source: Medical Tribune "Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia (VITT) Proposed"
Delivered at 2021:04 on September 14, 05
https://medical-tribune.co.jp/rensai/2021/0414536026/
■ There is also research into the extent of the risk of thrombosis from vaccinations.
There are also reports of investigations into whether there is a high risk of side effects from vaccination.
On April 2021, 4, a research team from the University of Oxford announced the results of an analysis showing that the risk of developing blood clots in the brain is 15 to 8 times higher from contracting the coronavirus without being vaccinated than from receiving AstraZeneca's COVID-10 vaccine.
A study based on a US medical database looked at cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) in 50 coronavirus patients and found the incidence rate to be 100 per million. Meanwhile, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has said the incidence rate after receiving the AstraZeneca vaccine is 39 per million.
According to Professor Maxime Thaquet of the University of Oxford, the mortality rate from CVST was the same, around 20%, whether one had been infected with Covid-XNUMX or vaccinated.
Source: Reuters "The risk of thrombosis due to coronavirus infection is 8-10 times higher than that of thrombosis due to vaccination"
https://jp.reuters.com/article/health-coronavirus-vaccines-clots-idJPL4N2M9229?il=0
In addition to this,
In the UK, simple maths shows that
The incidence of thrombosis after vaccination is about 25 in 1 people
- Death rate is about 100 in 1 million.
According to the Asahi Shimbun, comparing vaccine-induced thrombosis with other types of thrombosis,
About 2 in 1 women taking oral contraceptives
Economy class syndrome affects about 1 in 1 people
There are also reports that.
Therefore, as announced by European regulators,
"The overall benefits of vaccination are considered to outweigh the risks."
[10] Low-dose aspirin therapy may be effective
In addition to vaccines, research is also underway into treatments and measures to prevent the disease from becoming severe.
Let's take a closer look.
It has been found that taking low-dose aspirin reduces the risk of patients with coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-44) needing mechanical ventilation by XNUMX%.
Jonathan H. Chow and his colleagues from George Washington University in the United States conducted a multicenter cohort study of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 to examine the effects of aspirin on the progression of disease, such as the need for mechanical ventilation, and on outcomes, and published the results in Anesth Analg (2021; 132: 930-941).■ ICU admissions and in-hospital deaths also decreased
The study, which was published in the journal Cell Biology, is the first to investigate the effect of aspirin on the severity and outcome of COVID-19.
In the aspirin group,
Risk of needing a ventilator is 44%
The risk of ICU admission was reduced by 43%.
The authors concluded that "the use of low-dose aspirin was associated with a significantly reduced risk of mechanical ventilation, ICU admission, and in-hospital death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19." In addition, because aspirin has antiplatelet and anti-inflammatory effects, they inferred that "the lung-protective effect of aspirin may be enhanced in diseases such as COVID-19, which have a very high tendency to coagulate and cause vascular endothelial cell dysfunction," and that "the anti-inflammatory effect of aspirin may contribute to the lung-protective effect of COVID-19."
Source: Medical Tribune, "Aspirin reduces coronavirus ventilator placement by 44% - Multi-center cohort study of hospitalized COVID-19 patients in the U.S." Published on March 2021, 03 at 22:05 a.m.
https://medical-tribune.co.jp/news/2021/0322535723/
[11] Taiwan policy
Finally, let me introduce Taiwan's pandemic policy.
Some of you may have seen reports that Taiwan has successfully contained the new coronavirus by utilizing IT, and this "Taiwan model" reflects past experiences and lessons learned.
He said, "There are things we can do even without a vaccine."
I feel that this holds a variety of implications for Japan, which is currently experiencing its fourth wave of infections.
How Taiwan fought COVID-19: A memo from Taiwan's health minister
Drawing on its experience with SARS in 2003, Taiwan has implemented well-considered, swift and transparent response to COVID-XNUMX, which has led to the country being praised as the "Taiwan model" for COVID-XNUMX response.
Initially, Taiwan was expected to be the first to be affected by the COVID-19 outbreak that began in China, and to suffer devastating damage. However, appropriate measures were taken, and infections were almost exclusively limited to people entering the country from overseas, and no major local outbreaks occurred within Taiwan. Therefore, there was no need for a strict lockdown, and Taiwanese citizens were able to continue their lives almost as normal.Taiwan has leveraged its experience with SARS in 2003 to optimize its infectious disease control framework by reviewing its management system, laws, training, and relevant government mechanisms.
Learning from the SARS response, the government recognized that creating an effective command and control system was of utmost importance, and so established the Central Epidemic Command Center (CECC) to integrate various government agencies and prepare for future infectious disease outbreaks.Taiwan has established four principles for pandemic preparedness:
① Rapid response
2. Early deployment
3) Well-thought-out measures
④Transparency
By leveraging democratic processes, citizen cooperation, and technology, we have overcome many obstacles and created the "Taiwan model" for dealing with the pandemic.Several important measures were taken quickly early in the pandemic.
Following reports of multiple cases of pneumonia of unknown cause in Wuhan on December 2019, 12, emergency quarantine of people entering the country from Wuhan was initiated. Furthermore, on January 31, 2020, the CECC coordinated interagency cooperation and pooled resources essential to responding to the COVID-1 pandemic.
President Tsai Ing-wen convened a high-level national security meeting and issued a disease prevention directive on January 1.The WHO declared COVID-1 a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) on January 30, but Taiwan had already implemented a series of response measures.
For example, anticipating a shortage of masks due to panic, the Ministry of Economic Affairs ordered companies to increase production of masks in a short period of time.
In addition, the CECC instructed the Ministry of Transportation, the Immigration Bureau, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, and the Mainland Affairs Council to properly coordinate border control in response to the pandemic situation.
In order to prevent the spread of COVID-14, it is vital that those entering the country and their close contacts undergo home quarantine for XNUMX days.To implement these quarantine measures, we made full use of Taiwan's advanced information technology.
For example, they have created a system that records the information of all entrants and conducts quarantine checks.
To ensure that all people who should be quarantined at home remain in their quarantine area and provide support while respecting their privacy, we have developed a "digital fencing system" that obtains and tracks the location information of people who need to be quarantined via their mobile phones.
In addition, travel, occupation, close contact, and cluster exposure histories of each patient were available from Taiwan's comprehensive health insurance database.
Prefectural authorities have also set up care and support centres to provide food, medical care and counselling to all those in self-isolation.Measures need to be constantly reviewed in line with the pandemic situation.
For example, initially, people rushed to buy masks, which led to a shortage and spread panic.
We instructed companies to increase mask production and used our health insurance database to create a name-based mask distribution system for all citizens.
This has made masks available to everyone at a relatively low price.Furthermore, in early March 2020, the number of infected people in Europe increased dramatically beyond our expectations, and many Taiwanese citizens began to return home. This was expected to lead to an increase in infections in Taiwan.
In response, we increased our border control staff in mid-March, created a designated taxi system to transport returning travelers, and secured hotels for quarantine.
As a result of these efforts, we were able to prevent an increase in community infections due to returning residents.In Taiwan, measures to prevent infection must be backed by law and have public scrutiny.
To gain people's trust and support, since its establishment, the CECC has widely disseminated information about COVID-19 to the public through various media, including press conferences, and has corrected misinformation. The CECC's activities have been praised by the public.
The COVID-19 pandemic has taught us that we must always be prepared to respond to new infectious disease outbreaks.When an outbreak occurs, action needs to be taken quickly, and vaccines are the last resort in this battle.
At the start of the pandemic, Taiwan donated medical supplies to more than 80 countries in the spirit of "Taiwan Can Help and Taiwan is Helping!"
Furthermore, even without a vaccine, we believe that we can effectively contain this pandemic by utilizing digital technology. We hope that our experience will be of use to you.
Source: Chen SC (Ministry of Health and Welfare, Taipei, Republic of China (Taiwan))
“Taiwan's experience in fighting COVID-19”
Nature Immunology. 2021 Mar 26.
doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-00908-2. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 33772224
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41590-021-00908-2
Translation by Dr. Michiyuki Matsuzaki (Dohoku Kinikyo Asahikawakita Hospital)
*The content of this page is current as of July 2021, 4.