HPV vaccine
This is a vaccine to prevent human papillomavirus (HPV) infection (※1), which is related to the development of cervical cancer. It can prevent approximately 90% of HPV infections (※2), especially before the first sexual encounter. Any woman who has had sexual intercourse can become infected.
- 1 Human papillomavirus (HPV) is involved in the development of diseases such as cervical cancer, anal cancer, and vaginal cancer.
(reference:https://www.mhlw.go.jp/bunya/kenkou/kekkaku-kansenshou28/index.html) - 2. Vaccination Office, Health Bureau, Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
(reference:https://www.mhlw.go.jp/content/10601000/000838245.pdf)
Inoculation target person
- Vaccination is strongly recommended, especially for women, regardless of whether they are sexually active or not.
- We offer vaccinations to anyone aged 16 and over.
Types of HPV Vaccines
Two types of vaccines are available at our clinic. To be fully effective, both vaccines require three doses over a six-month period (initial vaccination, two months later, and six months later).
Sylgard®9
This vaccine was approved in Japan in 2020 and is effective against nine types of HPV, covering approximately 90% of the HPV types that cause cervical cancer.
Gardasil®
This vaccine was approved in Japan in 2011 and is effective against nine types of HPV, covering approximately 90% of the HPV types that cause cervical cancer.
| Vaccine Name | Sylgard®9 | Gardasil® |
|---|---|---|
| Number of virus strains to prevent infection | 9 | 4 |
| Target gender and age | Women over 16 | 16 years or older |
| Effect | Cervical cancer and its precancerous lesions, vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia, vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia, genital warts | Cervical cancer and its precancerous lesions, vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia, vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia, genital warts, anal cancer and its precancerous lesions |
| Inoculation number of times | 3 doses (first vaccination, second vaccination 2 months later, third vaccination 2 months later) | |
| Side reaction | Pain, itching, swelling, redness, headache, fever, feeling of heat, lump, numbness, nausea at the injection site, etc. usually disappear within a few days | Pain at the injection site, itchiness, swelling, redness, headache, and fever usually disappear within a few days. |
| Price | 1 session: 38,500 yen (tax included) 3-session set: 110,000 yen (tax included) | 1 session: 22,000 yen (tax included) 3 sessions: 66,000 yen (tax included) |
reference:"Cervical cancer prevention information site "Motomamorou.jp"'
About Cervical Cancer
What is cervical cancer?
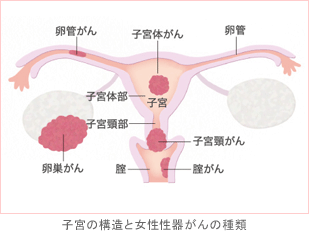
Cancer that develops in the cervix, which is near the entrance of the uterus, is called cervical cancer. The causes and process of cervical cancer have been largely elucidated, and it is a preventable cancer.
The cervical cancer vaccine does not prevent infection with all types of carcinogenic HPV. In order not to miss these abnormalities, it is necessary to undergo regular cervical cancer screening even after receiving the vaccine.
Frequently asked questions about the HPV vaccine
- How long do the effects of the HPV vaccine last?
Clinical trials conducted overseas have shown that three doses of the vaccine provide a preventive effect for about 3 years.
*3 ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier:NCT02653118- Is it effective for people who are already infected with HPV?
The vaccine can be administered to people who already have lesions (including genital warts) or who have had abnormalities on medical tests, but it will not improve existing lesions (1)(2).
Since the possibility of being infected with all of the HPV types included in the HPV vaccine is considered low, vaccination is well worthwhile in preventing disease caused by HPV types that are not present in the body (1)(2).
(1) Edited and supervised by the Japan Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology and the Japan Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Obstetrics and Gynecology Clinical Guidelines: Outpatient Gynecology. 2023:52-53.
(2)Markowitz LE et al. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2014;63(RR-05):1-30.
- What are the side effects of the HPV vaccine?
The main side effects reported are pain, swelling, erythema, itching, and internal bleeding at the injection site, and systemic side effects include headache, dizziness, oropharyngeal pain, nausea, diarrhea, fever, and fatigue. Although rare, severe symptoms (severe allergic symptoms, symptoms of the nervous system)* may occur.
- If I get the HPV vaccine, will I no longer need cervical cancer screening?
No, regular cervical cancer screening is still necessary even if you have received the HPV vaccine. Because the vaccine does not prevent all HPV-related cancers, early detection and early treatment through screening are important.
- Can I get this vaccination at the same time as other vaccinations?
Yes, the HPV vaccine can generally be given at the same time as other vaccines, but it is recommended that the vaccine be given in a different site (such as the other arm).



